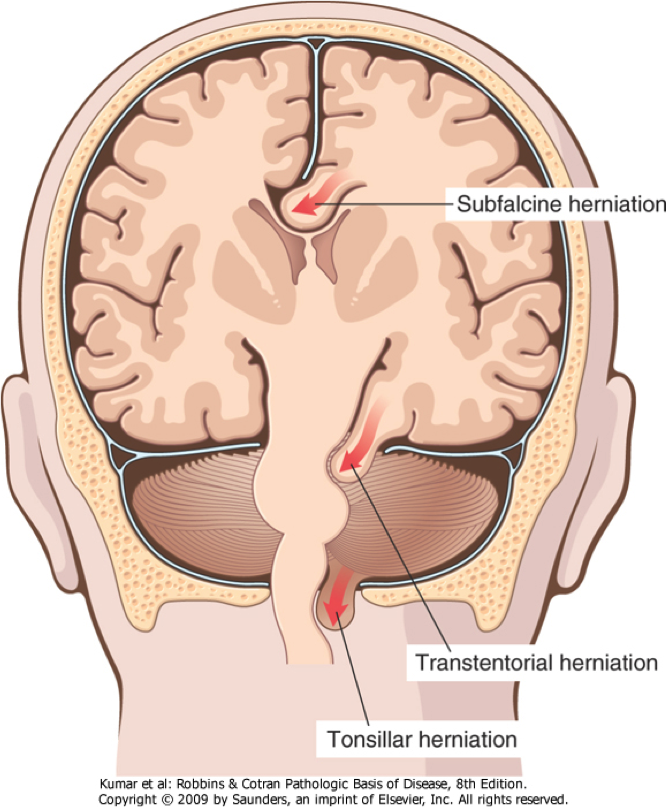
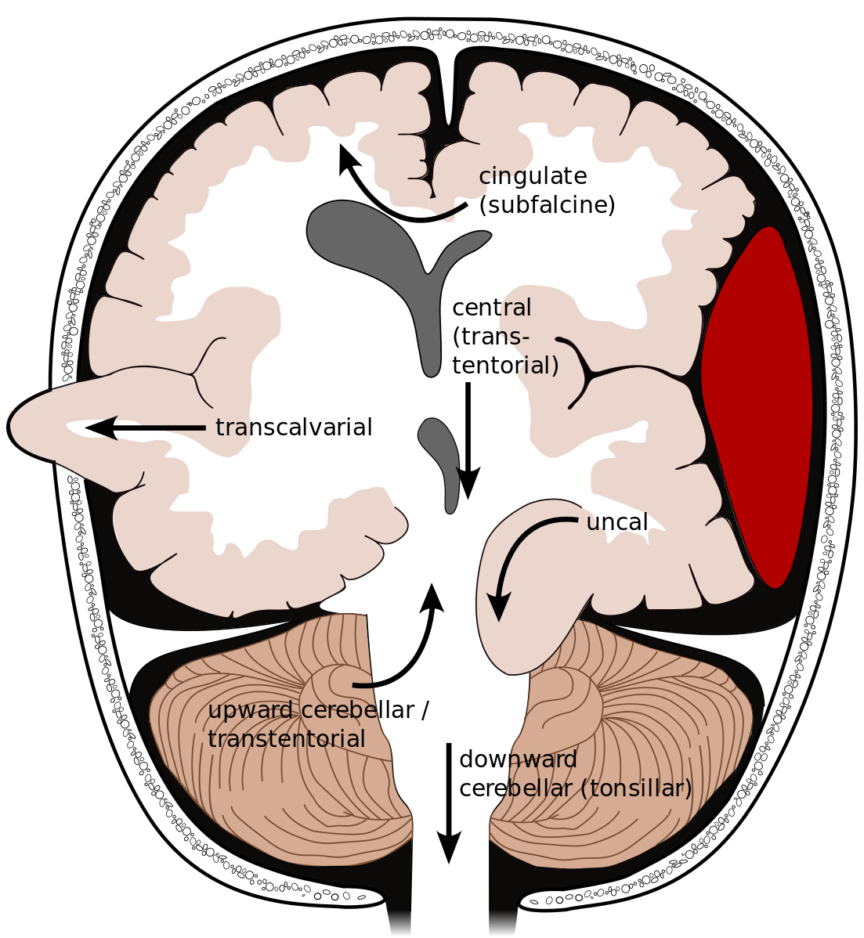
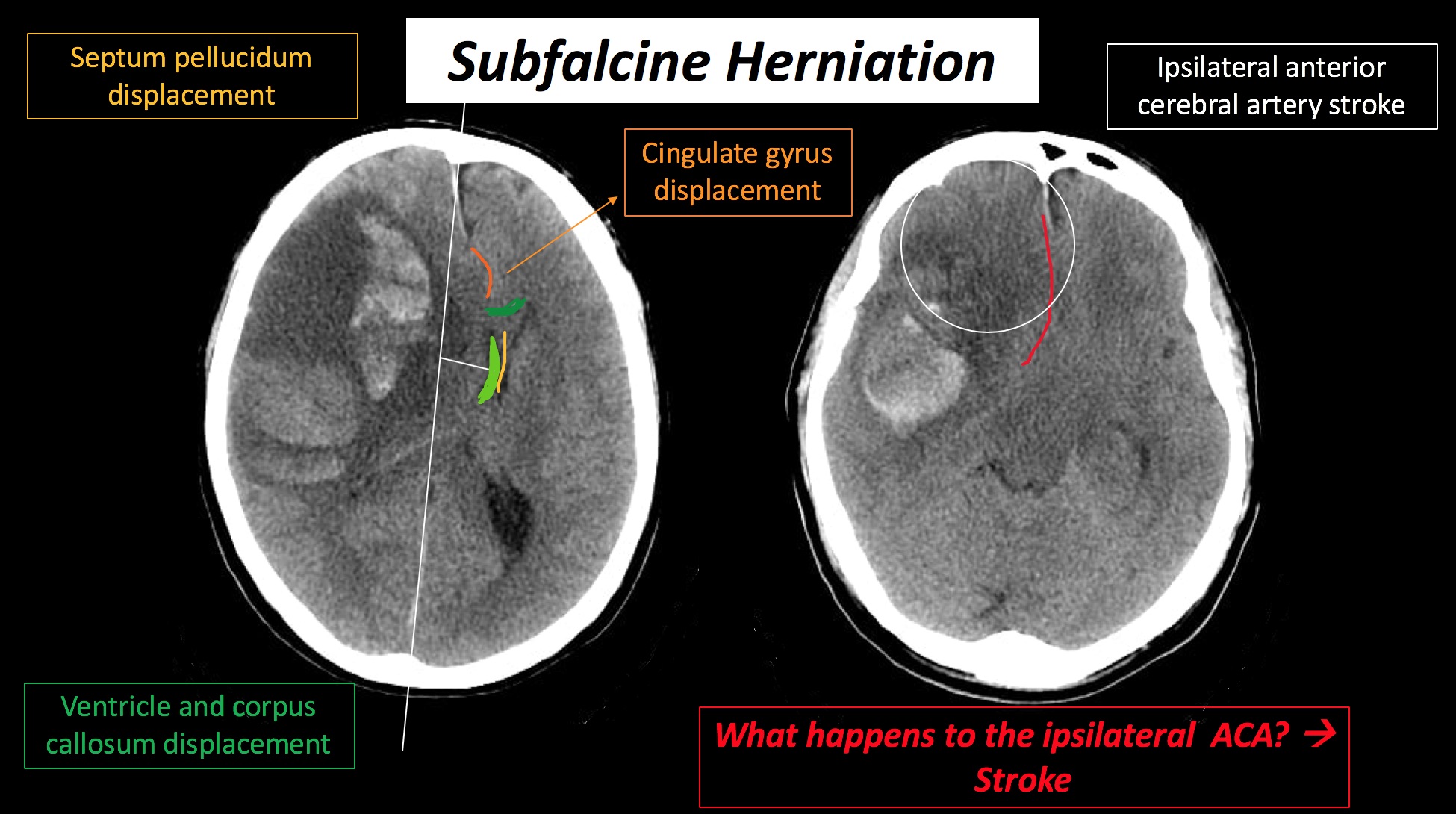
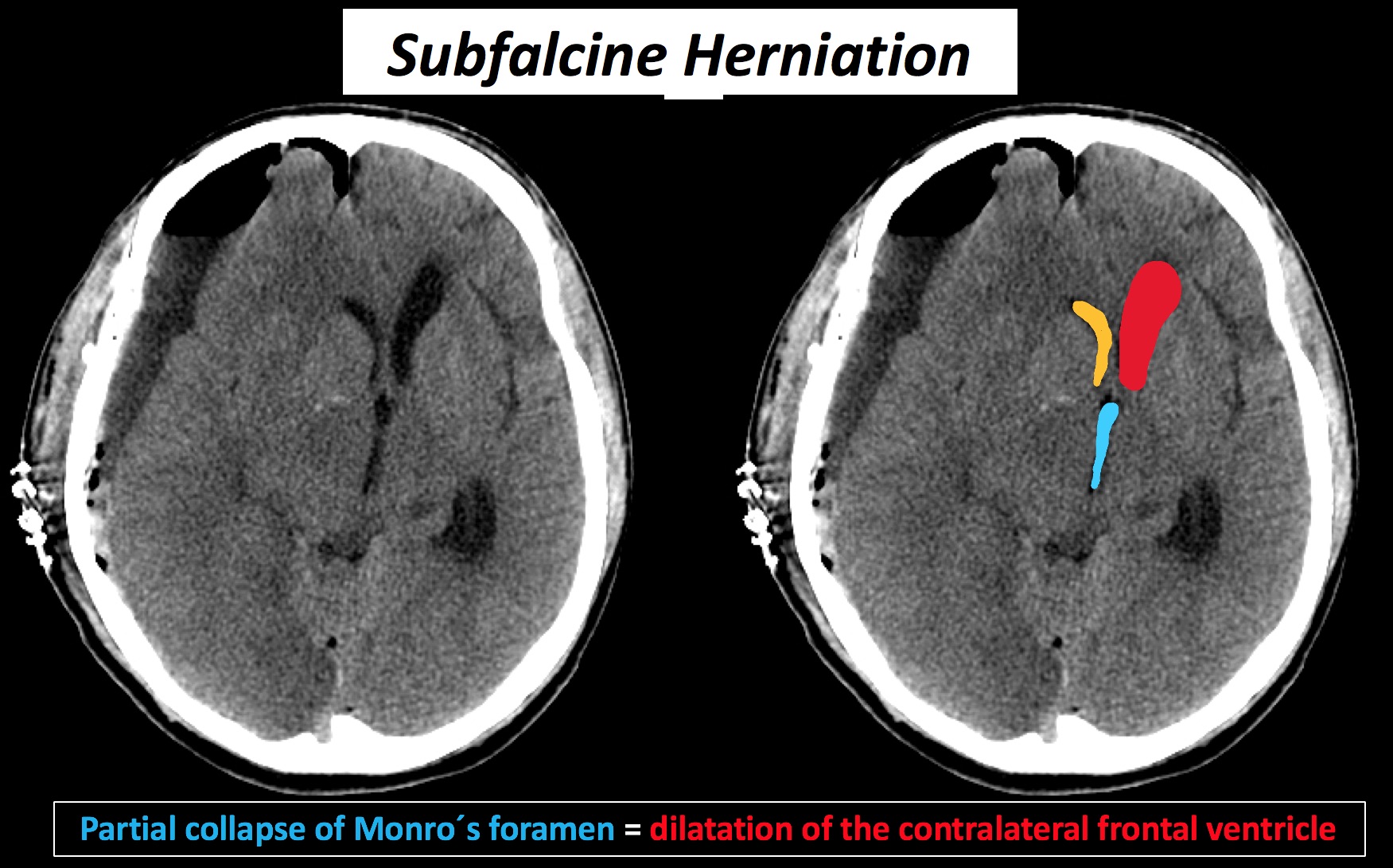
Subfalcine (Cingulate)
- CT : Displacement of the cingulate gyrus/septum pellucidum.
|
- Cingulate gyrus
- ipsilateral cingulate gyrus is pushed under the rigid midline falx
- Compression of the ipsilateral anterior cerebral artery
|
- Severe headache
- Contralateral leg weakness
|
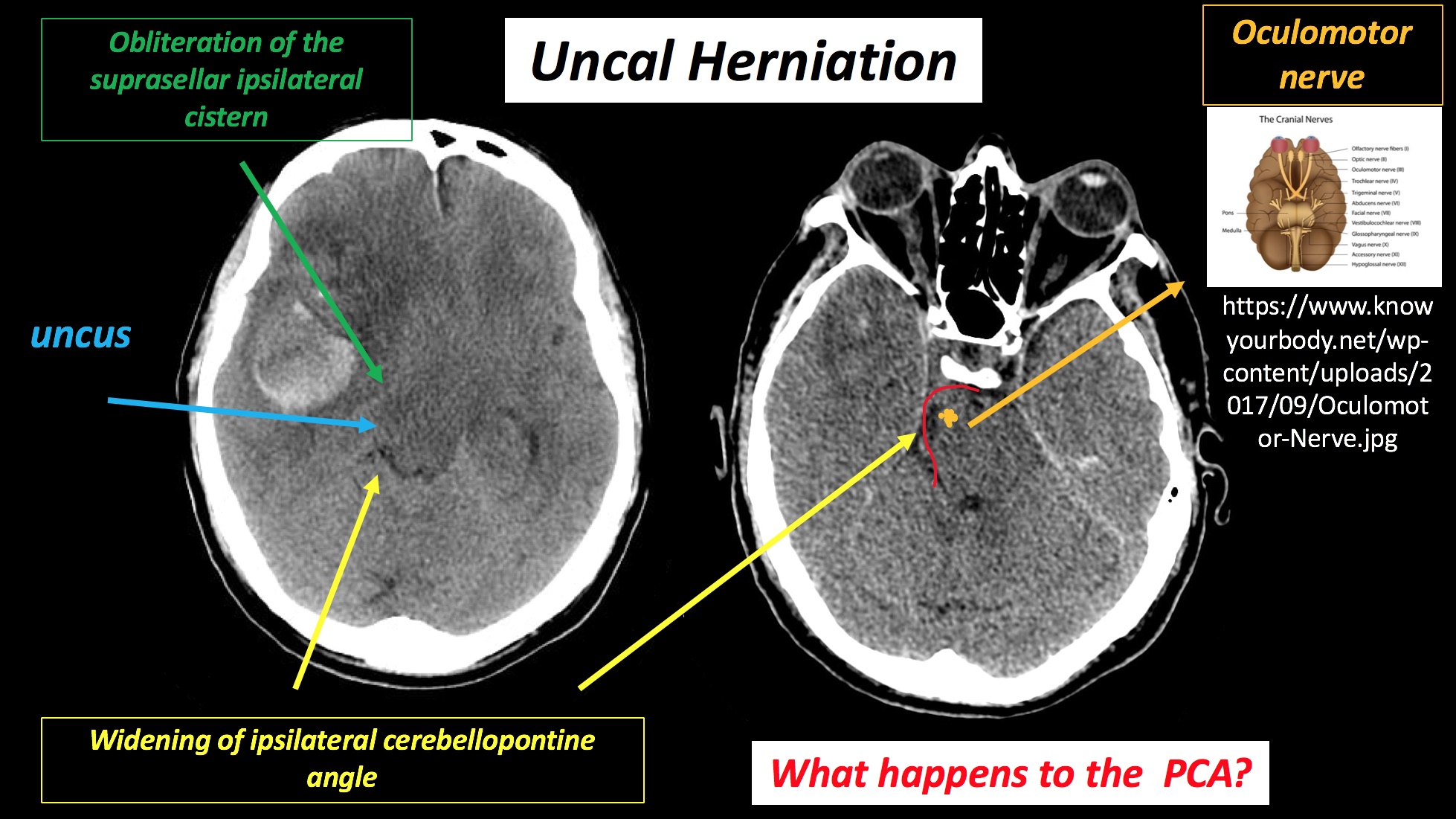
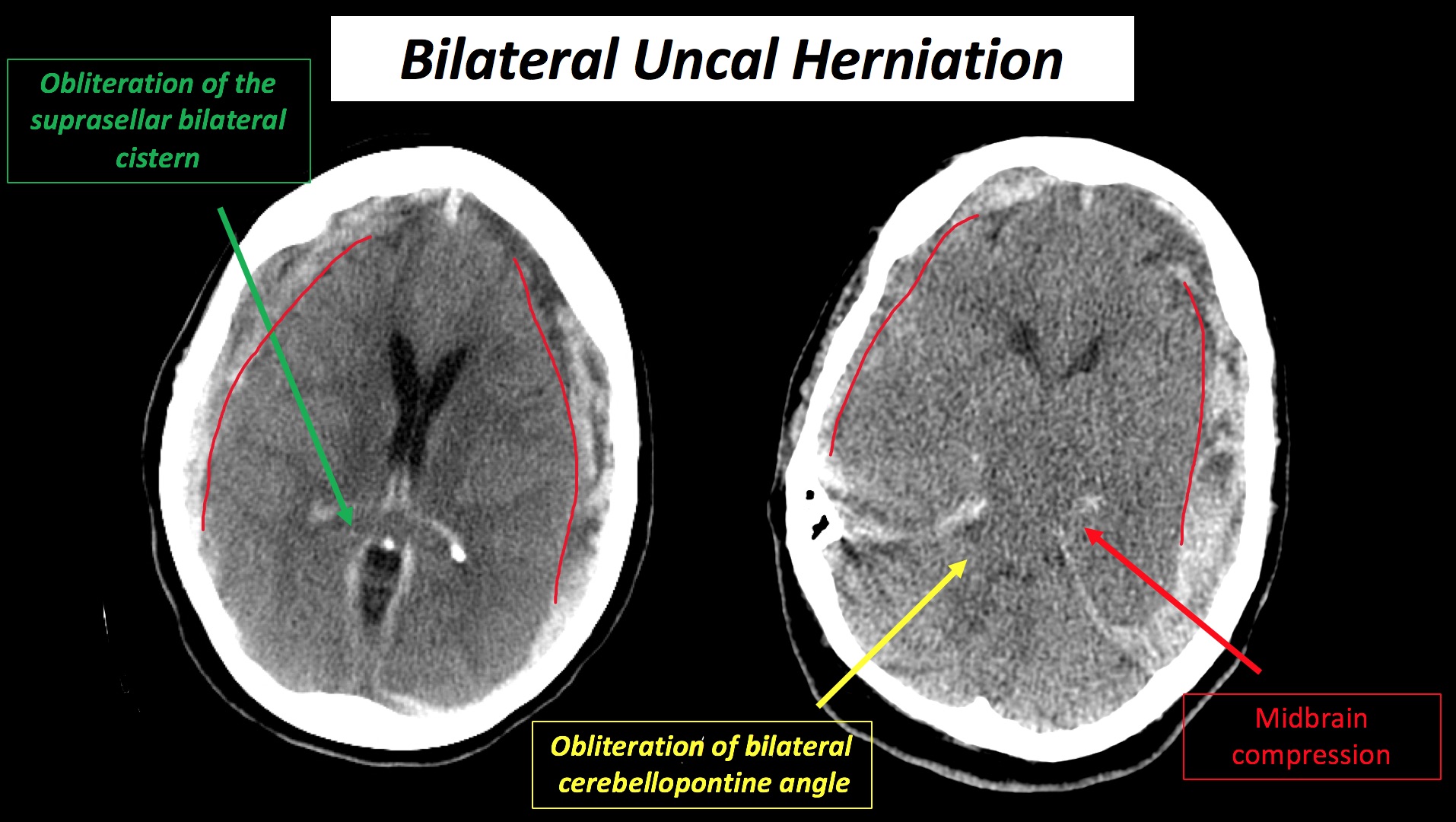
Lateral (Uncal)
- CT : Widening of the ipsilateral cerebellopontine angle and obliteration of the suprasellar ipsilateral cistern.
|
Uncus and the adjacent part of the temporal lobe (supratentorial structures) are displaced caudally across the tentorial incisura into the infratentorial compartment.
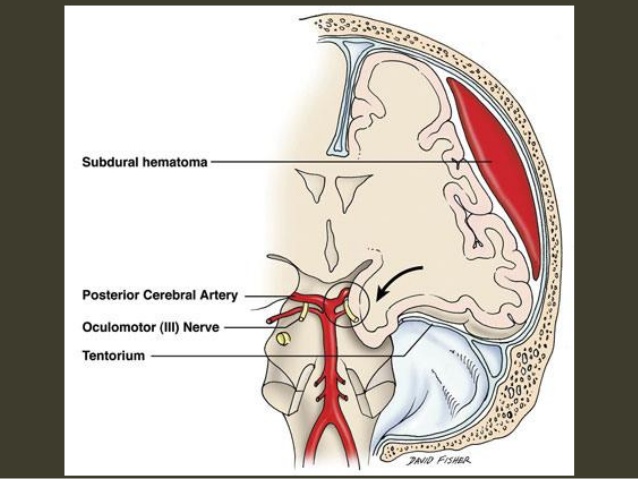
- ipsilateral Occulomotor n. (CN III)
- Cerebral peduncle
- ipsilateral posterior cerebral artery
|
- Ipsilateral Ptosis
- Ipsilateral Mydriasis (pupil โต)
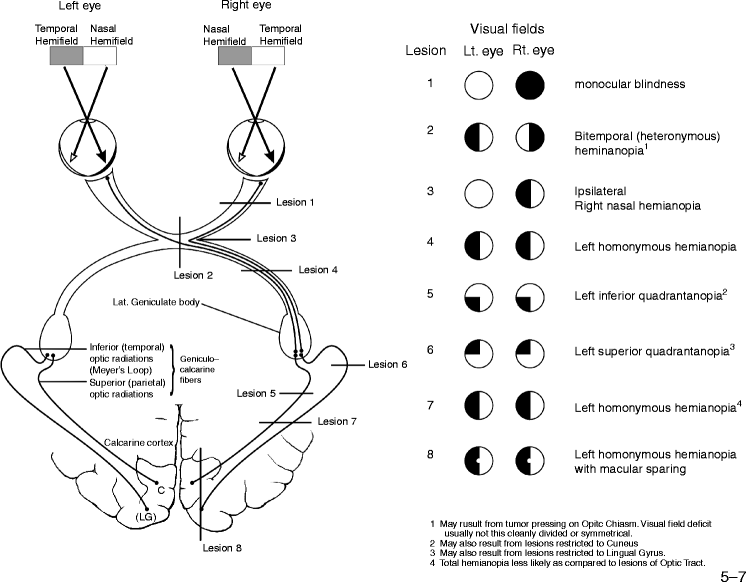
- Homonymous hemianopia
- Contralateral hemiparesis (Cerebral peduncle)
- Ipsilateral hemiparesis : Kernohan notch คือ pressure of free edge of tentorium against opposite cerebral peduncle
- Decreased consciousness
|
Posterior (Tectal) |
- Superior colliculi (Quadrigeminal plate)
|
- Bilateral ptosis
- Upward gaze paralysis
|
Central (axial) ie. Tonsillar herniation
- CT : effacement of the CSF cisterns surrounding the brainstem and inferior descent of the cerebellar tonsils below the foramen magnum.
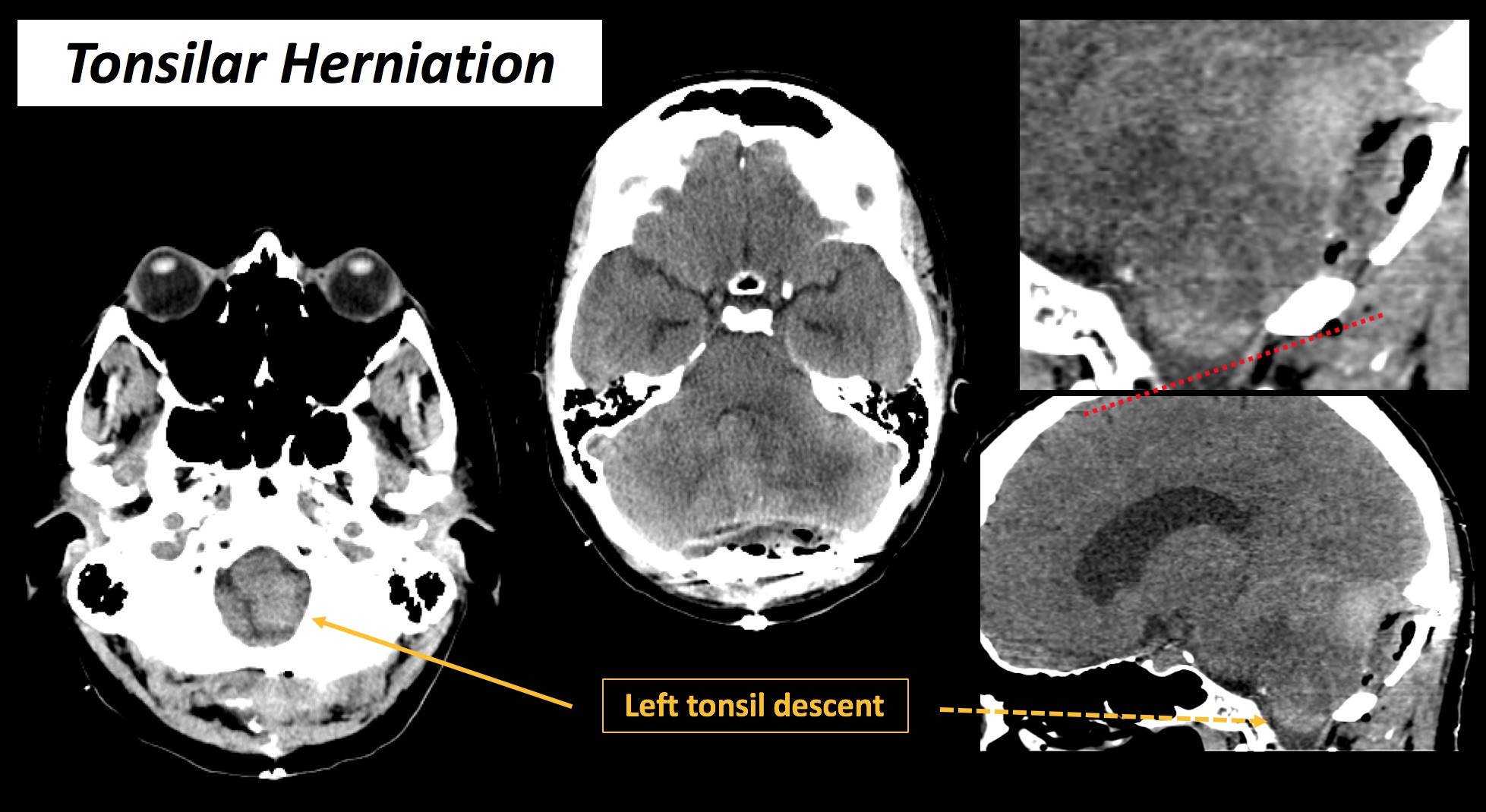
|
Inferior descent of the cerebellar tonsils below the foramen magnum.
Obstructive supratentorial hydrocephalus may result from fourth ventricle compression.
- Perforating branches from basilar artery
- Midbrain (mid brain)
- Pons
- medulla
- Reticular formation
|
- Decreased consciousness (Reticular formation)
- Decerebrate rigidity (M2) : Transection of midbrain
- Impaired eye movement
- Respiratory irregularity
- Apnea
- Hypertension (Wide pulse pressure : SBP สูง DBP ต่ำ)
- Bradycardia
** Cushing's reflex : Late compensate before heniation ได้แก่ Bradycardia, Wide PP, IICP
|