Big Data & Application in Business
International College of Digital Innovation, CMU
July 3, 2025
Why Do We Need Big Data?
When data is large enough, we can make more accurate decisions.
In statistics, these foundational theorems serve as the backbone of big data.
They justify why large datasets improve analysis, prediction, and decision-making.
Fundamental Theorem of Statistics
Assume that \(X_{1}, X_{2}, \ldots\) are independent and identically-distributed random variables in \(\mathbb{R}\) with common cumulative distribution function \(F(x)\). The empirical distribution function for \(X_{1}, \ldots, X_{n}\) is defined by \[ F_{n}(x)=\frac{1}{n} \sum_{i=1}^{n} I_{\left[X_{i}, \infty\right)}(x)=\frac{1}{n}\left|\left\{1 \leq i \leq n \mid X_{i} \leq x\right\}\right| \] where \(I_{C}\) is the indicator function of the set \(C\). For every (fixed) \(x, F_{n}(x)\) is a sequence of random variables which converge to \(F(x)\) almost surely by the strong law of large numbers, that is, \(F_{n}\) converges to \(F\) pointwise.
\[ \left\|F_{n}-F\right\|_{\infty}=\sup _{x \in \mathbb{R}}\left|F_{n}(x)-F(x)\right| \longrightarrow 0 \text { almost surely. } \]
Simulated Data
Law of Large Numbers
In this course, the weak law of large numbers is sufficient.
The weak law states that the sample mean converges to the expected value as the number of observations increases:
\[ \bar{X}_{n} \stackrel{P}{\rightarrow} \mu \quad \text{as } n \rightarrow \infty \]
That is, for any positive number \(\varepsilon\),
\[ \lim_{n \rightarrow \infty} \operatorname{Pr}\left(\left|\bar{X}_{n} - \mu\right| < \varepsilon\right) = 1 \]
As the sample size grows, the average of the observed values becomes increasingly close to the population mean.
Simulated Data
The 4Vs of Big Data
Big Data is defined by four key characteristics (4Vs), which describe its essential nature:
Volume: The sheer amount of data
Velocity: The speed at which data is generated and processed
Variety: The diversity of data types and sources
Veracity: The reliability and accuracy of data
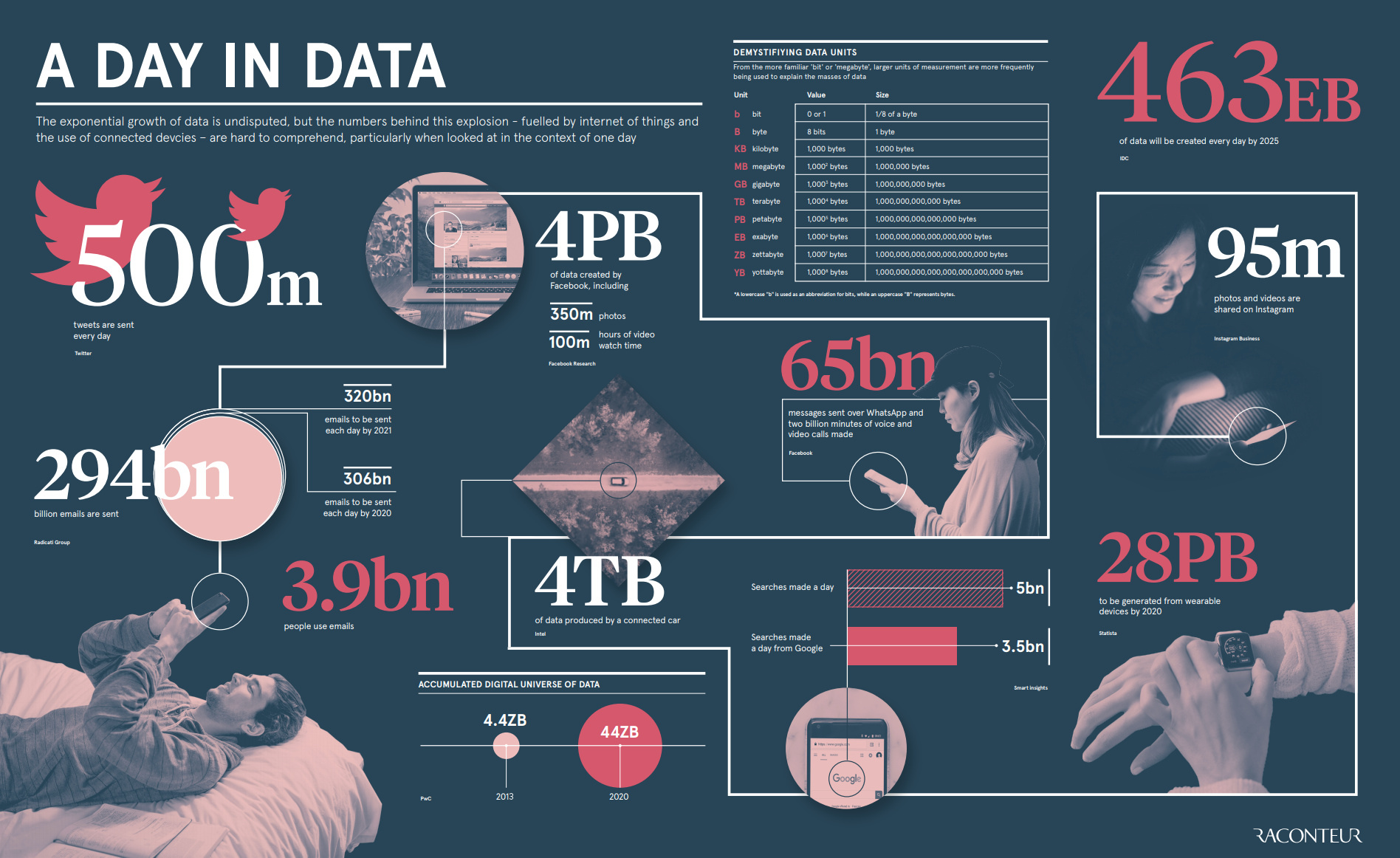
1. Volume
Big Data refers to data of extremely large volume, often measured in terabytes (TB), petabytes (PB), or exabytes (EB).
Examples
Facebook generates more than 4 petabytes of data per day from posts, comments, and photos
Banking systems process millions of transaction records every day
IoT devices produce massive volumes of sensor data in industrial settings
2. Velocity
Data is generated and flows into systems at high speed, requiring real-time processing.
Examples
The stock market needs to analyze stock price data in real time
Google uses Big Data to deliver search results in a fraction of a second
Streaming platforms like Netflix and YouTube must recommend videos in real time
3. Variety
In the Big Data era, data isn’t limited to just numbers or text— it also includes images, videos, audio, and unstructured data.
Examples
Structured Data: Customer databases, transaction records
Semi-Structured Data: JSON or XML files, web data
Unstructured Data: Social media posts, YouTube videos, CCTV images
4. Veracity
Big Data often contains inaccurate or unreliable information (Noise & Uncertainty), so data must be verified and filtered carefully for accuracy.
Examples
Fake reviews on e-commerce platforms like Amazon or Shopee
Misinformation from social media, such as fake news
Transaction data with errors that must be cleaned before analysis
Summary: The 4Vs of Big Data
| V | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Volume | Massive amount of data generated and stored | Facebook generates 4+ PB/day of posts, photos |
| Velocity | Speed at which data is created and processed | Stock market updates, real-time video suggestions |
| Variety | Different types and formats of data | Text, images, videos, audio, IoT sensor data |
| Veracity | Reliability and quality of data | Fake reviews, social media misinformation |
Tip: Big Data becomes powerful only when we can manage all 4Vs effectively — collecting, processing, understanding, and trusting the data.
Big Data In 5 Minutes (Simplilearn)
Businesses That Make Money from Big Data
1. Technology & Social Media
Platforms with massive user bases generate enormous volumes of data, which are used to analyze user behavior and drive revenue.
Examples
Google (): Uses search behavior data to deliver targeted ads via Google Ads
Facebook (): Sells ads based on user behavior and interests
TikTok (), YouTube (): Analyze viewing behavior to recommend personalized content
2. E-Commerce & Retail
These businesses leverage Big Data to analyze buying behavior and personalize ads, promotions, and product recommendations.
Examples
Amazon (), Lazada, Shopee: Analyze customer behavior to improve personalized product recommendations
Walmart, Lotus, BigC: Uses AI to calculate real-time inventory levels
Alibaba: Applies Big Data to predict consumer trends
3. Financial Services & Banking
Big Data is used to analyze spending behavior, detect fraud, and forecast market trends.
Examples
Visa (), Mastercard (): Analyze transactions to detect and prevent fraud
Goldman Sachs, JPMorgan Chase: Use AI to predict stock market trends
Various banks: Assess customer risk before issuing loans
4. Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals
Big Data is used to analyze patient data, conduct drug research, and predict disease outbreaks.
Examples
Pfizer, Moderna: Use AI to analyze DNA data for vaccine development
IBM Watson Health: Uses Big Data to assist doctors in diagnosing and recommending treatments
Major hospitals: Analyze patient data to plan personalized treatments
5. Logistics & Transportation
Big Data is used to optimize delivery routes, reduce transportation costs, and manage inventory efficiently.
Examples
DHL (), FedEx (), UPS (): Use AI to calculate the fastest delivery routes
Grab: Analyze travel data to adjust fares dynamically
Airlines: Use Big Data to forecast travel demand and adjust ticket pricing
6. Media & Entertainment
Big Data is used to analyze audience behavior and create personalized content experiences.
Examples
Netflix, Disney+, Spotify (): Analyze viewing and listening data to recommend content
ESPN, Twitch (): Use Big Data to analyze sports statistics and deliver real-time content
7. Energy & Utilities
Big Data is used to monitor energy usage and forecast environmental trends.
Examples
Tesla: Analyzes data from electric vehicles to improve autonomous driving systems
Energy companies: Use AI to predict electricity and oil demand
8. Education & EdTech
Big Data is used to analyze learning behavior and develop personalized, effective curricula.
Examples
Coursera, Udemy: Use AI to analyze student data and recommend suitable courses
Schools and universities: Use Big Data to analyze student performance and academic outcomes
Summary: Industries Using Big Data to Generate Revenue
| Industry | Use of Big Data | Example Companies |
|---|---|---|
| Technology & Social Media | Advertising, user behavior analysis | Google, Facebook, TikTok |
| E-Commerce & Retail | Product recommendations, purchase analysis | Amazon, Shopee, Walmart |
| Finance & Banking | Risk analysis, fraud prevention | Visa, JPMorgan, Goldman Sachs |
| Healthcare & Pharma | Patient analytics, drug research | Pfizer, Moderna, IBM Watson Health |
| Logistics & Transportation | Route optimization, dynamic pricing | DHL, Uber, Grab |
| Media & Entertainment | Audience behavior analysis | Netflix, Disney+, Spotify |
| Energy & Environment | Forecasting energy demand | Tesla, various energy companies |
| Education | Learning analytics, personalized courses | Coursera, Udemy, Duolingo |
Extended: 5V and 6V of Big Data
Sometimes, two additional elements are added to the core 4Vs:
Value (The business value of data): High-quality data can drive business value, such as through personalized marketing.
Variability (The changing nature of data): Data constantly changes in volume, type, and meaning—requiring AI or machine learning to interpret effectively.
Leading Companies in Big Data Infrastructure
These companies are key players in developing the infrastructure and tools that support Big Data operations. They provide both hardware and software solutions that enable organizations to store, analyze, and utilize large-scale data efficiently.
1. Big Data Hardware Providers
These companies develop servers, storage units, and processing chips designed to support large-scale data processing.
| Company | Key Products | Revenue Source |
|---|---|---|
| IBM | IBM Power Systems, IBM Storage | Servers for Big Data, Cloud Computing |
| Dell Technologies | Dell EMC PowerEdge, Dell EMC Isilon | Enterprise-level storage solutions |
| Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) | HPE Apollo, HPE Nimble Storage | Servers and storage for AI & Big Data |
| NVIDIA | GPUs (Tesla, A100, H100) | AI/ML processors for Big Data Analytics |
| Intel | Intel Xeon Processors | CPUs for servers and data centers |
| Western Digital & Seagate | HDDs, SSDs for Data Centers | Large-scale storage devices |
| Cisco | Cisco UCS, Cisco Nexus | Networking and server systems for Big Data |
Revenue Streams:
Selling servers and storage devices to enterprises
Selling GPUs and CPUs for large-scale data processing
Providing infrastructure services through cloud and data centers
2. Big Data Software Providers
These companies build tools and platforms for storing, analyzing, and managing large-scale data.
| Company | Key Software/Platforms | Revenue Streams |
|---|---|---|
| BigQuery, Google Cloud Storage | Cloud-based data warehouse, AI & ML analytics | |
| Amazon (AWS) | Amazon Redshift, AWS S3, AWS Glue | Cloud computing and data lake services |
| Microsoft | Azure Synapse Analytics, Microsoft SQL Server | Cloud & enterprise data solutions |
| IBM | IBM Watson, IBM Cloud Pak for Data | AI-driven analytics, machine learning services |
| Oracle | Oracle Big Data SQL, Oracle Cloud | Database & cloud-based Big Data solutions |
| Snowflake | Snowflake Data Cloud | Cloud data warehouse with data sharing capabilities |
| Cloudera | Cloudera Data Platform (CDP) | Big Data analytics with Hadoop & Spark |
| Databricks | Databricks Unified Data Analytics Platform | AI & data science platform built on Apache Spark |
| Palantir | Palantir Foundry, Gotham | AI-powered enterprise Big Data analytics |
| Splunk | Splunk Enterprise | Data monitoring, observability & security analytics |
Revenue Streams:
Providing cloud-based Big Data analytics via subscription models
Selling licensed data analytics software to businesses
Offering AI and machine learning solutions for enterprises
Selling platforms that support data integration and governance
3. Top Industry Users of Big Data
In addition to hardware and software providers, some companies generate direct revenue by applying Big Data in their operations.
| Industry | Key Companies | How They Use Big Data to Generate Revenue |
|---|---|---|
| Social Media & Advertising | Google, Facebook, TikTok | Analyze user behavior to sell targeted ads (Google Ads, Meta Ads) |
| E-Commerce & Retail | Amazon, Alibaba, Walmart | Customer analytics, dynamic pricing, recommendation systems |
| Financial Services | JPMorgan, Goldman Sachs, Visa | Transaction analysis, fraud detection, AI-driven trading |
| Logistics | FedEx, Uber, Grab | Optimize delivery routes and ride-matching efficiency |
| Healthcare & Pharma | Pfizer, Moderna, IBM Watson Health | Patient data analysis, drug discovery and R&D |
| Energy & Environment | Tesla, Shell, Siemens | Predict energy demand, develop smart vehicles and infrastructure |
4. Innovative Startups in Big Data
In addition to large enterprises, startups are also using Big Data to drive innovation.
| Company | Solution | How They Use Big Data |
|---|---|---|
| DataRobot | AI-based Machine Learning Automation | Develops an AI platform to help businesses build ML models faster |
| H2O.ai | Open-source AI & AutoML | Enables businesses to create AI models without coding |
| Alteryx | Self-service Data Analytics | Offers easy-to-use data analytics tools |
| Confluent | Apache Kafka-based Event Streaming | Provides a platform for real-time streaming data |
| Fivetran | Cloud-based Data Integration | Simplifies data movement from multiple sources to data warehouses |